poniedziałek, 5 sierpnia 2013
There is a basophil in the center of the field which has a lobed nucleus (like PMN's) and numerous coarse, dark blue granules in the cytoplasm. They are infrequent in a normal peripheral blood smear, and their significance is uncertain. A band neutrophil is seen on the left, and a large, activated lymphocyte on the right.
sobota, 27 lipca 2013
Subskrybuj:
Komentarze (Atom)




+CML+with+a+large+quantity+of+micromegakaryocytes+(cells+%E2%80%93+4A,+B,+C,+D;+5A,+B,+C,+D;+6A,+B,+C,+D).jpg)



+is+a+rare,+congenital+disorder+which+causes+a+bleeding+disorder.+The+platelets+are+large+and+have+a+grey+appearance+on+light+microscopy.png)






,+band+neutrophils+(2),+two+lobed+neutrophil+(3)+and+neutrophils+(4).jpg)

+and+numerous+coarse,+dark+blue+granules+in+the+cytoplasm.jpg)
.jpg)













.png)
.jpg)
.jpg)




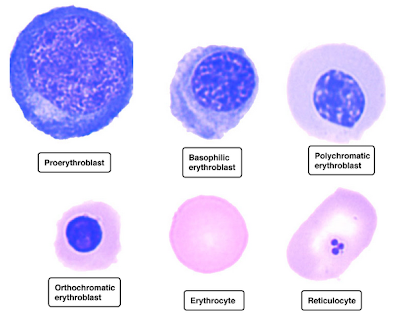




+with+highly+basophilic+cytoplasm+and+a+perinuclear+halo.png)




